An anal fissure is a longitudinal split in the anoderm (anal skin) of the distal (far end) anal canal. Endoderm is the epithelium lining of the anal canal up to the dentate line.
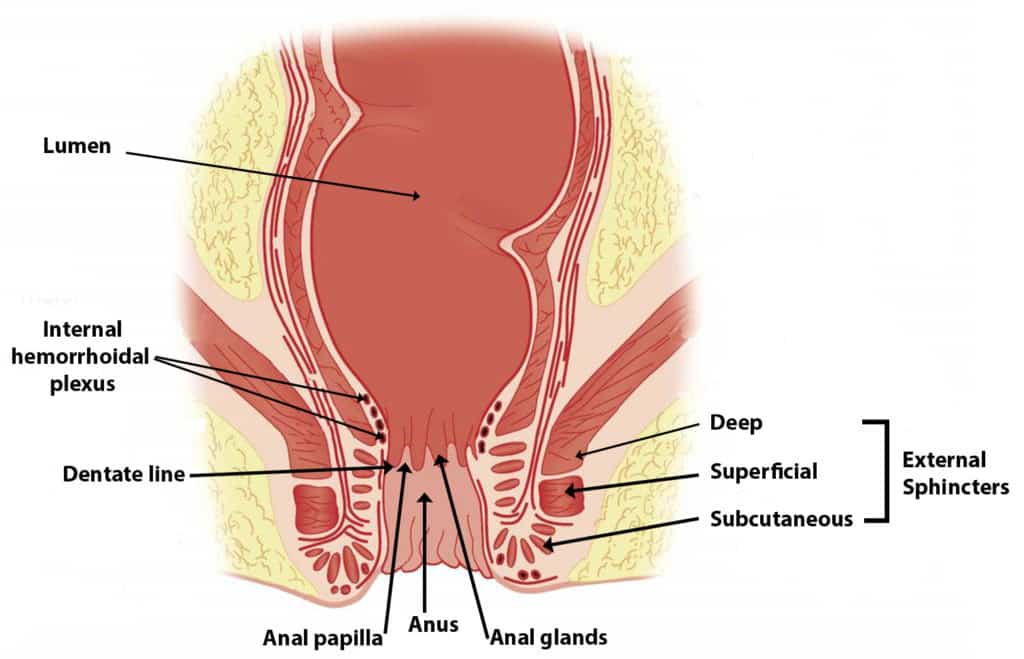
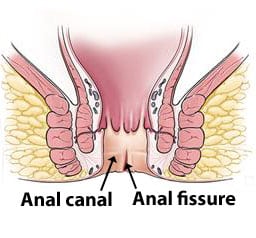
Anal fissures extend from the anal verge to upward. But it does not extend beyond the dentate line of the anus.
This affects all age groups, from infant to elder. But most common in young adults. It affects both men and women equally.
An anal fissure can categorize as acute and chronic according to the cause and symptoms.
Acute anal fissure
It is a recent onset fissure which is less than two weeks duration.
Causes of acute anal fissure
- Strained evacuation of hard stool
- A most common cause for acute anal fissure is the strained evacuation of hard stool. It leads to a split of the anoderm (anal skin).
- Less commonly repeated passage of diarrhea cause an acute anal fissure.
- Normal vaginal delivery
The most commonplace for acute anal fissure is the posterior midline of the anal circumference. When defecation exaggerated, shearing forces act to the posterior (back) midline of the anal canal. Their endoderm is less elastic. Also, the presence of the longitudinal muscle density is higher than in other places of the anal canal. So the shearing force will cause a split and make a posterior midline fissure.
An anterior anal fissure can see in 10 % of women and 1% in men. Anterior fissure happens due to vaginal delivery. That’s why it more common in females.
Symptoms
- Sever pain-in the acute anal fissure
- It involves sensitive anoderm.
- So sever anal pain feels after and with defecation. Until a few hours after defecation, the pain will last.
- The pain will resolve spontaneously after hours. But again, it will reappear at the next defecation.
- Fresh blood passing with defecation. Usually, it notices when wiping from a tissue.
Chronic anal fissure
In a chronic anal fissure, scar tissue (hypertrophied anal papilla ) presence inwardly from the anus. Sentinel tag can see outwardly from the anus. (hood like a skin tag and cover the fissure)
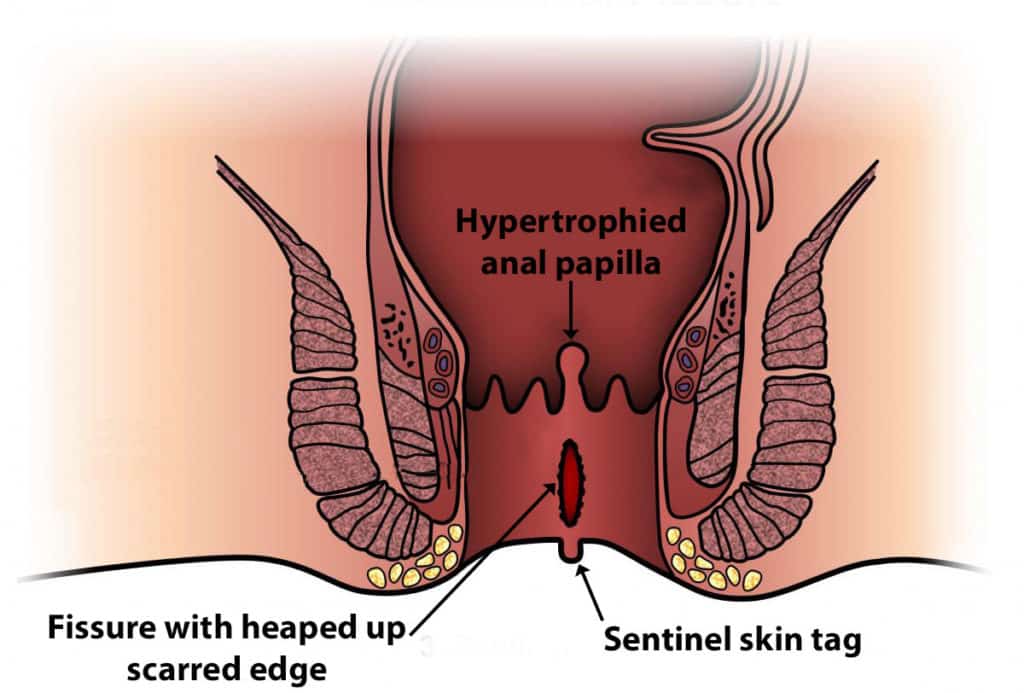
Causes of chronic anal fissure
- Repeated trauma to the anal canal.
- Frequent healing and breaking of the anal fissure lead to chronic fissure.
- Anal hypertonicity.
- Increase the tone (tightness) of the anal sphincter
- Vascular insufficiency.
- Poor blood supply leads to poor healing of the trauma. It leads to developing chronic anal fissure.
Symptoms
- Itching from the anus.
- Itchiness happens because the irritation occurs in the external sentinel tag.
- Discharge from the ulcer
Usually, the healthy person who is having normal sexual behavior only has anterior anal fissure and posterior anal fissure. If a person has anal fissure sited elsewhere around the anal circumference or presence of atypical fissure, that person needs to be investigated for various other diseases such as Tuberculosis, Chrons disease, and Sexually transmitted disease.
- An anal fissure can be seen in patients with below diseases and conditions.
- Sexually transmitted disease ( That patient may do anal sex. Anal sex is a cause for anal fissure)
- Crohn’s disease
- Tuberculosis
- Vaginal delivery
- Anal sex
- Passing hard stools
- Previous anal surgery
Due to vaginal delivery, anal sex, and passing hard stools, trauma occurs in the anal area. So anal fissure occurs.
Treatment (Management)
- There are three types of management.
- Conservative management
- Medical management
- Surgical management
Conservative management
The first-line treatment method is conservative management. There less traumatic stool passage is created. Stool softeners, adequate water intake, and fiber diet to bulk up the stool are conservative methods. Using a conservative method helps to heal chronic and acute fissures.
Medical management
In medical management, pain reducers and topical applications use for relaxing the anal sphincter.
For pain reduction, a topical anesthetic agent applies to the anus. Also, a warm bath helps to decrease the pain caused by fissures.
Anal sphincter relaxer, reduce spasm of the anus and so reduce pain. Reducing spasm increases vascular perfusion (blood supply to the anal is increased). It promotes healing.
Example– GTN (Nitric oxide donors) 0.2% applied four times per day. Diltiazem 2% cream applies in the morning and evening.
Surgical management
In surgical management, the aim is to decrease the anal sphincter tone (tightness). But the surgical method causes the sphincter to relax permanently. It leads to developing fecal incontinence (stool pass without voluntary control). Due to this, the surgical method is discouraged, and it uses only when conservative and medical management failed.
