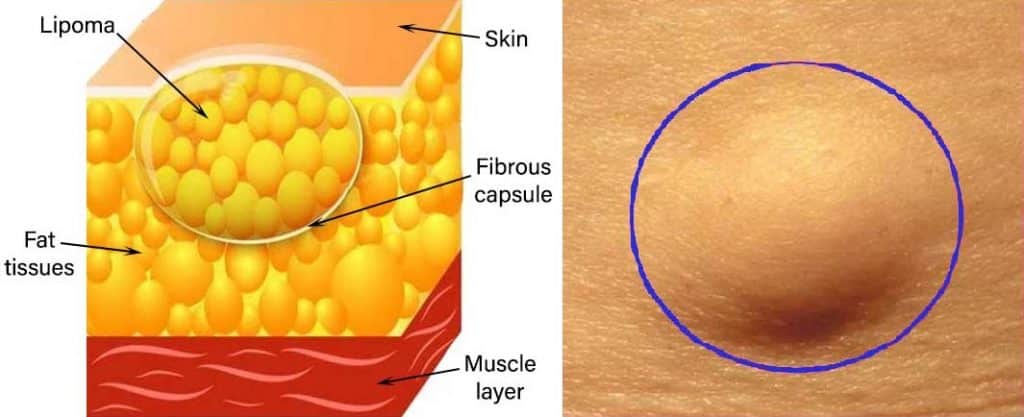
What is Lipoma
A lipoma is a cluster of fat cells that become overactive and so distended with fat. So it will feel like palpable lumps. Lipoma contains soft but solid jelly-like fat.
It can either be,
- Subcutaneous or
- Intramuscular
Subcutaneous
The subcutaneous lipoma is not attached to superficially or deeply. So it can move all directions.
Muscular
The muscular lipoma is fixed deeply. It is noticeable if the lipoma is pushed out of muscles (e.g. when the muscles are contracting).
Locations of Lipoma
Lipomas are not malignant (cancerous). It can occur in almost all ages. But less incidence in the children.
Usually, lipomata are growing very slowly. Due to its slow growth, it may take several years or months to notice.
- Lipomas can present anywhere in the body. But the most common in the subcutaneous tissues of the,
- Upper limbs
- Chest
- Neck
- Shoulder
Symptoms
Most patients present to the doctors when they notice a lump and need to know about it. If the lump is large, it may interfere with the movement.
Sometimes these patients may have a history of excised (removed) lipoma in the past. Some may have multiple lipomata. This condition is known as lipomatosis, and it usually presents in the buttocks and neck. Most often, it isn’t painful.
Examination findings
- The overlying skin of the lipoma is normal.
- Usually, the lipoma is spherical shapes.
- But when it presents between the skin and the deep fascia, it can be discord or hemispherical.
Lipomas come in all sizes, and most lipomas are lobulated. Fibromata lobules surround by fine strands of fibrous tissue. Also, it isn’t transilluminating or fluctuate. But physical signs of pseudo fluctuation and pseudo transillumination make them appear cystic, giving a false impression.
Transillumination
Transillumination is the passing of an intense beam of light through a part of the body for medical inspection. Light will pass easily through a clear fluid but not through solid tissues. A lump that transilluminate must contain water, sebum, lymph, or plasma. Blood and other opaque fluids do not transmit light. When transilluminated, light shines entirely through the body part.
Fluctuation
Fluctuation is a wave-like motion or insulation of fluid in a natural or abnormal cavity that is felt during palpation or percussion.
A percussion wave is efficiently conducted across a large fluid collection(cyst). But not across a solid mass. Fluctuation is detected by tapping one side of the lump and feeling the transmitted vibration when it reaches to the other side.
- Examples of fluctuation are
- pus in an abscess
- fluid-filled lump
Treatment for lipoma
If the lipoma is not going to affect patients day to day life, there is no need to treat it. But if it’s uncomfortable to the patient or if it’s the patient’s request, the following methods are used to treat lipoma.
- Liposuction – Remove through a tiny incision
- Surgical excision under local anaesthesia.
Lipoma needs to correctly excise. Otherwise, it can reappear.

Pingback: Varicose veins - Symptoms, Causes and Treatments - MedFog