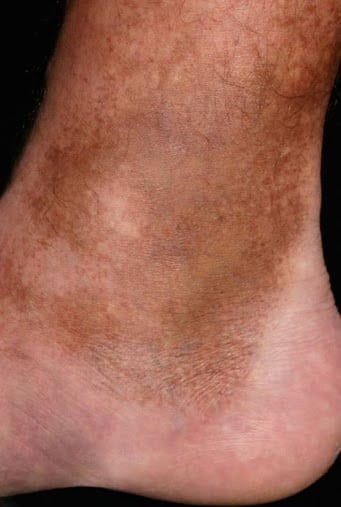
Hemosiderin staining
Due to some circumstances, cells may accumulate abnormal amounts of various substances. Those accumulations can be harmless, or it can cause varying degrees of injuries. When an excessive amount of haemoglobin is stored as hemosiderin inside the cells, Hemosiderin staining occurs. It is one branch of Intracellular accumulations. So, in order to understand Hemosiderin staining, we need to look at the Intracellular accumulations.
Intracellular accumulations
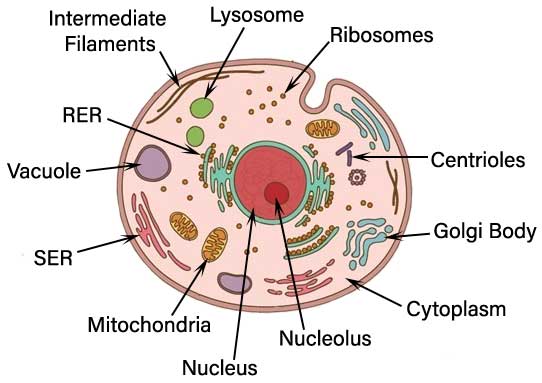
When cells accumulate an abnormal amount of various substances, it is called Intracellular accumulation. The substances can either located in the cytoplasm of the cells within organelles or in the nucleus.
Pathways of intracellular accumulation
- There are four main pathways of abnormal intracellular accumulations.
- Inadequate removal of an ordinary substance
- Accumulation of an abnormal endogenous substance
- Failure to degrade(break down)a metabolite
- Abnormal Deposition and accumulation of exogenous substances
Pigments
There are several types of intracellular accumulators, and pigments are one of them. Pigments are colored substances. They are either from outside of the body (exogenous) like carbon or synthesized within the body by itself (endogenous). Those pigments are melanin, lipofuscin, carbon, and derivatives of hemoglobin.
Carbon
Carbon is the most common exogenous pigment. For example, we can consider coal dust. It is an air pollutant of urban life. When inhaled, it is phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages. (lung cells macrophages).
Macrophages are a type of white blood cells that engulf and digest cellular debris, foreign bodies, and anything which are not specific to healthy body cells. This engulfing mechanism is known as phagocytosis.
Lipofuscin
Lipofuscin is an insoluble brownish-yellow granular intracellular material. It accumulates in a variety of tissues, including heart muscles, liver, and brain. Lipofuscin is a complex of lipid and protein that derive from polyunsaturated lipids. When lipofuscin present in a large amount in a tissue, that is called Brown Atrophy.
Melanin
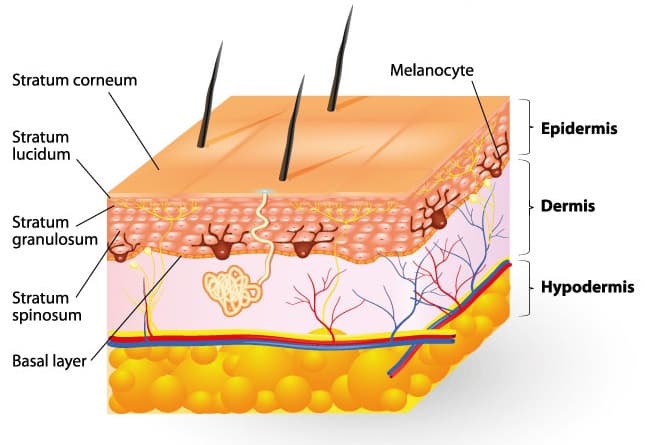
Melanin is a brown-black pigment synthesized by Melanocytes located in the epidermis. Melanin act as a screen against harmful ultraviolet radiation. It can accumulate in the basal keratinocytes in the skin.
Hemosiderin
Hemosiderin is hemoglobin derived granular pigment. Haemosiderin is golden yellow to brown color, and it accumulates in tissues when the iron is in excess.
How Hemosiderin staining occurs
Hemoglobin present in the red blood cells. They are responsible for carrying oxygen to the cells. When red blood cells are broken down, hemoglobin is released. The body needs to absorb hemoglobin back. So hemoglobin is broken down to heme and globin.
Further breakdown of heme produces iron and biliverdin. Hemosiderin is an iron storage complex. When the iron is excess in the body, Hemosiderin accumulations occur in tissues. White blood cells (part of the immune system) can reduce some of the excess iron. But when the iron is too much, it deposits and causes a visible stain in the skin.
Common conditions associated with Hemosiderin staining
- The following conditions are the most common among patients with Hemosiderin staining.
- venous ulcers
- trauma
- leg edema
- high blood pressure
- cardiovascular disease
- diabetes
Treatments for Hemosiderin staining
Staining in the skin is not a severe issue. But the underlying reason for staining (for an e.g. diabetes) the critical issue. Patients need to consult a doctor to identify and treat the root cause.
However, if you are interested in removing the staining, the following options are available.
- Laser therapy
- topical creams
Laser therapy
Laser therapy usually has to use more than one session. The number of sessions will be decided on the deepness of the darkness. Laser therapy use to remove skin stainings.not in organs staining.
Topical creams
Some use topical creams to remove haemosiderin staining in the skin. But it’s not effective. Because topical creams will not penetrate deep enough to remove the staining, only the laser can penetrate that layer of the skin, so if anyone wants to get rid of skin discoloration by haemosiderin staining, better to consider about the laser therapy.
Hemosiderosis
Excessive deposition of haemosiderin in tissues called Hemosiderosis.
- Since aging red blood cells degrade in below places, Hemosiderosis can see in,
- Bone marrow
- Spleen
- Liver
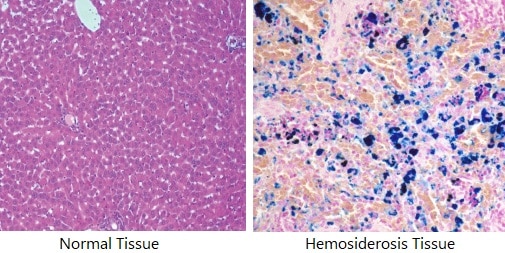
When a tissue sample is stained with Prussian blue, haemosiderin turns into a characteristic blue color. So it can be identified under a light microscope.
- Hemosiderin can see in
- repeated blood transfusion patients.
- idiopathic pulmonary Hemosiderosis
- after bleeding to the brain can see in brain tissues
- paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
- thalassemia patient and sickle cell disease patients who are undergoing repeated blood transfusion.
- This excess of iron accumulation in tissues is toxic.
- Heart deposition leads to heart failure.
- Liver deposition leads to liver failure, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
- When deposition in the endocrine organs, it leads to growth retardation due to
- hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- diabetes
- hypothyroidism
- hypoparathyroidism
Treatment of Hemosiderosis
- Immune suppression
- Limiting blood transfusion
- Iron chelation therapy
Iron chelation therapy increases iron excretion in urine and faeces with chelators.