What is an Ankle Sprain
An ankle sprain is common injuries that cause when the ankle is roll, twist or turn in an awkward way. This awkward movement can stretch or tear the ligaments. Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that help to hold ankle bones together.
Ligaments of ankle joint
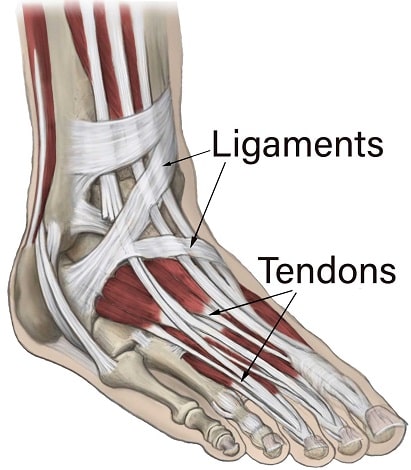
Ligaments are the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It supports the joints. But it does not connect muscles to bones. Muscles connect to the bones by tendons. The ankle joint has a lot of ligaments.
Ankle ligaments can divide into the medial ligament and lateral ligament.
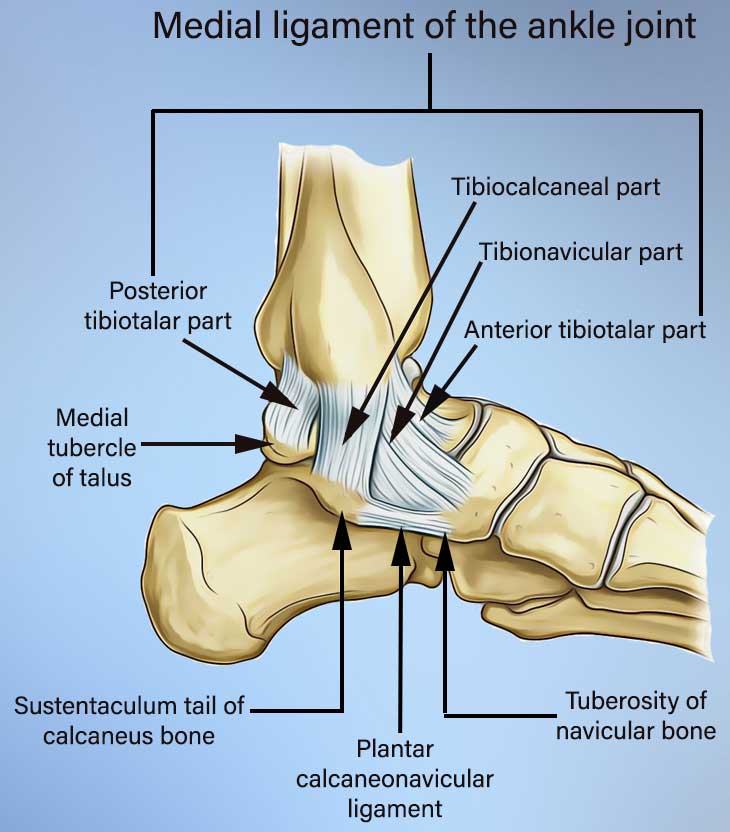
Medial ligament
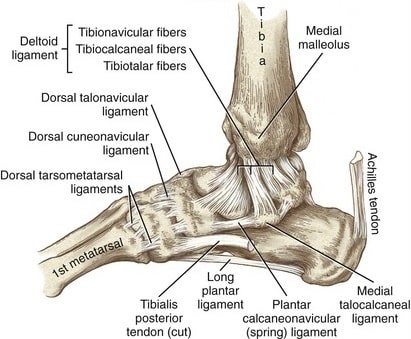
- Medial ligament of the ankle joint
- Deltoid ligament
- Calcaneonavicular ligament
The deltoid ligament is a triangular-shaped strong ligament on the medial side of the ankle.
Lateral ligament
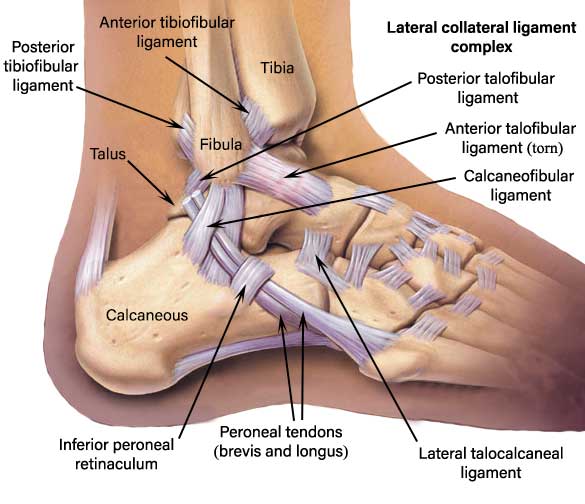
- Lateral ligaments of the ankle joint
- Syndesmosis ligament
- Anterior talofibular ligament
- Posterior talofibular ligament
- Calcaneal fibular ligament
- Lateral talocalcaneal ligament
Movement of the ankle joint
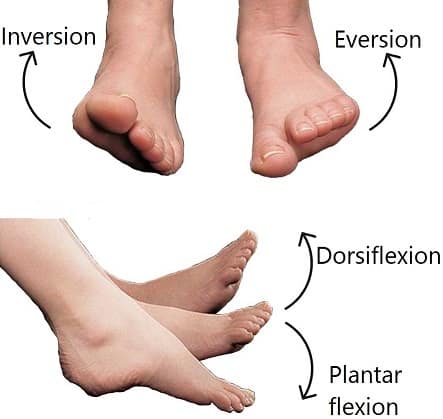
- Movement of the ankle joint
- Inversion
- Eversion
- Dorsiflexion
- Plantar flexion
- Eversion/Abduction forces cause trauma to the medial ligament complex of the ankle.
- Inversion/Abduction forces lead to injury of the lateral ligament complex.
Grades of ankle sprain
Injuries commonly occur in the Anterior talofibular ligament and the Calcaneo fibular ligament. These injuries can categorise as Grade 1, Grade 2 and Grade 3.
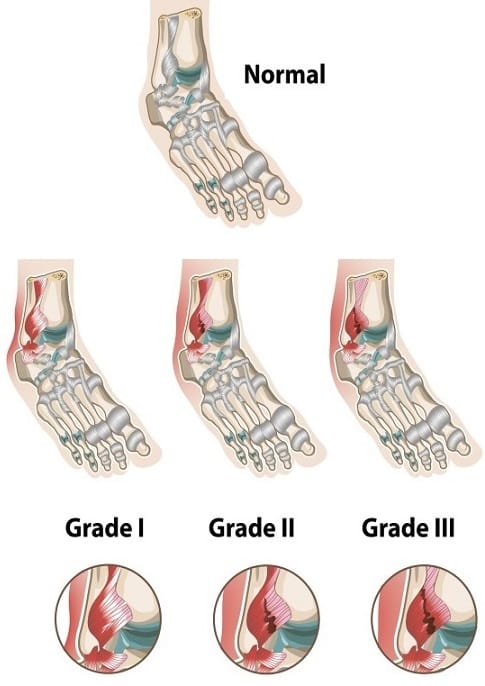
- Grades of ankle sprain
- Grade 1
- Minor ligamentous injury
- Grade 2
- Incomplete ligamentous injury
- Grade 3
- Complete disruption of a ligament or multiple ligaments
- Grade 1
Diagnosis of ankle sprain
Diagnose of an ankle sprain are difficult in acute(sudden onset) stage. So ankle joint is reassessed after 4 to 7 days after the incidence. MRI imaging of the ankle joint help to diagnose lateral ligament injuries with 90% accuracy.
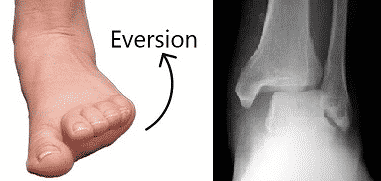
Usually, Medial ligament rupture occurs with disruption of the Syndesmosis ligament. Rupture of these two ligaments leads to the lateral shift of the talus on everting the ankle.
Treatment for the Ankle Sprain
The treatment for the Ankle Sprain aims to provide a stable ankle with good anatomical alignment and proper function.
- In grade 1 and grade 2 ankle sprain treatments are,
- Provide protection to ankle using ankle brace of strapping
- early mobilization
- the functional range of motion exercise
- Neuromuscular retraining exercise directed by a physiotherapist. This help to provide a stable ankle with a good range of movement.
- In grade 3 ankle sprain,
- Immediate surgical repair is the treatment for this grade injury. But the ruptured ligaments can require a secondary repair even after a few years.
Based on the injured tendon, treatment is slightly different.
Peroneal tendon injuries
Injuries to the peroneal tendon in ankle sprain is rare. If an injury happened, it is low-grade sprains(e.g. grade 1). For peroneal tendon injury, treatments are bracing and physiotherapy.
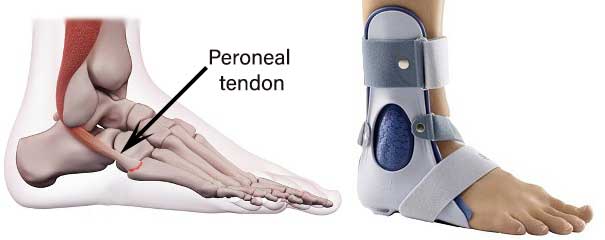
Bracing is used to support the ankle.
Complete ruptured peroneal tendons require surgical repair.
Tibialis posterior injuries
When the Tibialis posterior injured, pain around the medial ankle and hindfoot is common. The pain increases when exercise.
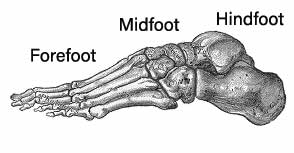
For the identification purpose, foot bone is divided into three parts. They are forefoot midfoot and hindfoot.
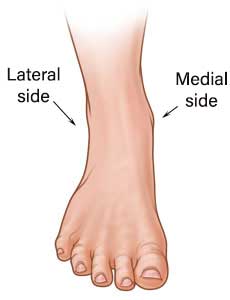
Based on the midline of the body, medial and lateral sides are defined.
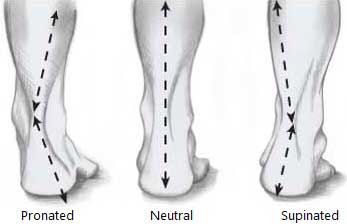
If tibialis posterior injury is untreated and the foot remains in a chronically pronated position, this pain can shift laterally.
Treatment for the injury is orthotic shoe implants or splinting to improve the foot position. In severe cases, surgical repair is needed.
Tibialis anterior ligament injuries
In this injury, acute inflammation within the tendon sheath (tendon sheath is a membrane that wraps around the tendon) of the tibialis anterior tendon occurs. It is a common injury among long-distance runners, and it causes pain, swelling and crepitus over the tendon. But it resolves with rest and rehabilitation.
Achilles tendon injuries
In Achilles tendon injury, pain and swelling of the Achilles tendon occur.
- There are two types of Achilles tendon inflammation.
- Chronic (long period) Achilles tendon inflammation.
- It develops microtears in the Achilles tendon and causes to lose its organized structure.
- Acute Achilles tendon inflammation.
- It occurs due to a sudden increase in activity which involves the Achilles tendon. It is common in athletes and who infrequently participate in sports.
- Physiotherapy with stretching and strengthening exercises is beneficial.
- If the case fails to respond to conservative measures, it may require surgical repair.
- Chronic (long period) Achilles tendon inflammation.
Feeling of a sharp blow to the back of the ankle and an inability to dorsiflex the foot are the characteristic of Achilles tendon rupture. Tears at the musculotendinous junction can be treated conservatively. (By using a plantarflexed cast or boost for 9 weeks)